Inbound Marketing Versus Digital Marketing
Marketing has evolved significantly over the past few decades, adapting to changes in technology and consumer behavior. Two prominent strategies that have emerged in the digital age are inbound marketing and digital marketing. While they share some similarities, they represent different approaches to engaging with consumers and achieving business goals. This analysis delves into the core principles, methodologies, benefits, and applications of inbound marketing and digital marketing to highlight their distinctiveness and interrelationship.
Understanding Inbound Marketing
Definition and Core Principles
Inbound marketing is a strategy focused on attracting and engaging customers through valuable content and experiences tailored to their needs and interests. Unlike traditional marketing, which often relies on interruptive techniques, inbound marketing aims to draw customers in by providing solutions to their problems and answering their questions.
The core principles of inbound marketing include:
- Attraction: Drawing in potential customers through engaging and relevant content.
- Engagement: Nurturing leads through personalized communication and interaction.
- Delight: Providing exceptional experiences to turn customers into advocates.
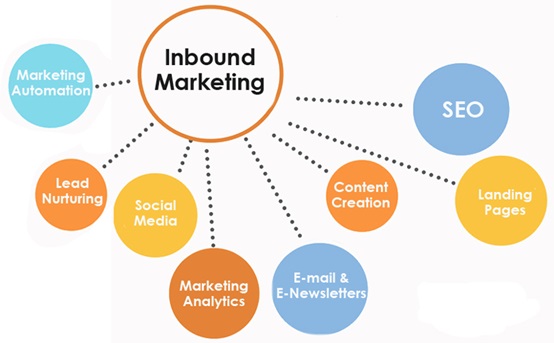
Methodologies and Tactics
Inbound marketing involves several key tactics:
Content Marketing: Creating blog posts, articles, eBooks, whitepapers, and videos that address the interests and pain points of your target audience.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimizing content and website structure to rank higher in search engine results, making it easier for potential customers to find your content.
Social Media Marketing: Using social platforms to distribute content and engage with your audience.
Email Marketing: Sending targeted emails to nurture leads and maintain relationships with existing customers.
Lead Generation: Using forms, landing pages, and calls-to-action to capture information from potential leads.
Benefits of Inbound Marketing
Cost-Effectiveness: Inbound marketing often requires a lower budget compared to traditional marketing methods, such as paid advertisements.
Long-Term Value: High-quality content can continue to attract leads over time, providing ongoing benefits.
Enhanced Engagement: By providing value and addressing customer needs, inbound marketing fosters stronger relationships with potential and existing customers.
Measurable Results: Metrics such as website traffic, lead conversion rates, and customer satisfaction can be tracked to gauge effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations
Time-Consuming: Building and maintaining an inbound marketing strategy requires significant time and effort to create and optimize content.
Initial Slow Results: It may take time to see significant results, as building authority and attracting organic traffic can be gradual.
Content Saturation: The increasing amount of content available online means that creating standout, high-quality content is more challenging.
Understanding Digital Marketing
Definition and Core Principles
Digital marketing encompasses a broad range of online marketing activities and channels aimed at reaching and engaging consumers through digital platforms. It leverages the internet and electronic devices to promote products and services and can be seen as a subset of overall marketing strategies that includes both inbound and outbound tactics.
The core principles of digital marketing include:
- Reach: Expanding the audience base through various digital channels.
- Engagement: Interacting with users to foster relationships and drive conversions.
- Conversion: Turning interactions into measurable business outcomes, such as sales or leads.
- Analysis: Using data and analytics to measure performance and optimize strategies.
Methodologies and Tactics
Digital marketing includes a diverse array of tactics and channels:
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Using paid ads on search engines and social media to drive traffic to your website.
- Display Advertising: Placing banner ads and visuals on websites to increase brand awareness.
- Affiliate Marketing: Partnering with affiliates to promote your products in exchange for a commission on sales.
- Social Media Advertising: Running targeted ads on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
- Email Marketing: Sending promotional emails to engage with potential and existing customers.
- Content Marketing: (Overlaps with inbound) Creating and distributing valuable content to attract and retain customers.
Benefits of Digital Marketing
Targeted Reach: Digital marketing allows for precise targeting based on demographics, interests, and behavior.
Scalability: Campaigns can be scaled up or down based on performance and budget.
Real-Time Analytics: Immediate access to performance data enables quick adjustments and optimization.
Flexibility: A variety of channels and tactics can be used to reach different segments of the audience.
Challenges and Considerations
Ad Fatigue: Consumers may become overwhelmed or desensitized to constant digital ads, reducing their effectiveness.
Privacy Concerns: Increasing scrutiny and regulations around data privacy can impact targeting and tracking.
High Competition: The digital space is highly competitive, making it challenging to stand out.
Comparing Inbound and Digital Marketing
Scope and Approach
Inbound Marketing: Focuses on attracting and engaging customers through valuable content and experiences. It is more about building long-term relationships and providing value upfront.
Digital Marketing: Encompasses a broad range of online activities, including both inbound and outbound tactics. It aims to reach and convert audiences through various digital channels.
Audience Engagement
Inbound Marketing: Engages customers by providing solutions to their needs and interests. It often involves a more personalized and content-driven approach.
Digital Marketing: Can engage customers through both content-driven and paid tactics, aiming for immediate visibility and interaction.
Strategy and Implementation
Inbound Marketing: Emphasizes organic methods such as content creation, SEO, and social media engagement. It requires a strategic focus on nurturing leads and building trust.
Digital Marketing: Utilizes a mix of organic and paid methods, including PPC, display ads, and social media marketing. It offers a broader toolkit for reaching and converting customers quickly.
Measurement and ROI
Inbound Marketing: Success is measured through metrics such as content performance, lead generation, and customer engagement. ROI can be long-term and cumulative.
Digital Marketing: Performance is tracked through a wide range of metrics, including ad performance, website traffic, and conversion rates. ROI can be more immediate and directly attributable to specific campaigns.
Conclusion
Inbound marketing and digital marketing are integral components of a modern marketing strategy, each with its own strengths and applications. Inbound marketing focuses on attracting and nurturing customers through valuable content and personalized experiences, while digital marketing encompasses a broader spectrum of online tactics, including both inbound and outbound methods.
Organizations should consider their goals, target audience, and resources when choosing between or integrating these strategies. Often, a balanced approach that combines the strengths of both inbound and digital marketing can yield the most effective results, leveraging the benefits of each to create a comprehensive and dynamic marketing strategy.
By understanding the distinctions and synergies between inbound marketing and digital marketing, businesses can better tailor their efforts to meet the evolving needs of their audience and achieve their marketing objectives.