What Skills Are Needed in Digital Marketing?

Digital marketing is a dynamic field that encompasses a variety of skills to effectively promote products or services online. Whether you’re a novice looking to break into the industry or a seasoned professional aiming to stay competitive, understanding the core skills required can help you navigate and excel in this space. Here’s an in-depth look at the key skills needed in digital marketing:
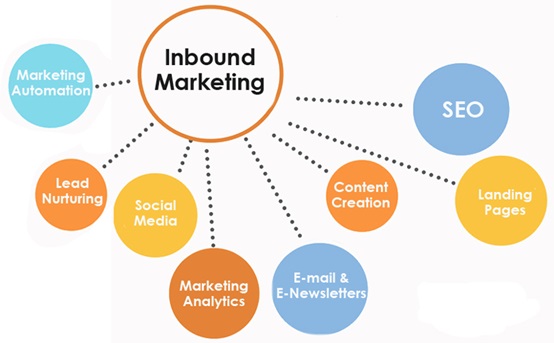
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
On-Page Optimization: Crafting content, meta descriptions, headers, and URL structures to improve rankings.
Technical SEO: Ensuring that a website’s technical aspects, like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability, are optimized.
Link Building: Acquiring high-quality backlinks to enhance a site’s authority and ranking.
SEO Analytics: Using tools like Google Analytics and Search Console to track and analyze SEO performance.
Content Marketing
Content Creation: Writing compelling and persuasive content, such as blog posts, articles, and social media updates.
Content Strategy: Planning and managing content to meet business goals and resonate with the target audience.
Content Distribution: Utilizing channels like email, social media, and websites to distribute content effectively.
Content Analytics: Measuring the effectiveness of content through metrics like engagement rates, shares, and conversions.
Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing focuses on leveraging platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to connect with audiences and promote products or services. Essential skills are:
Platform Proficiency: Understanding the unique features and algorithms of different social media platforms.
Social Media Strategy: Developing and implementing strategies for content creation, scheduling, and audience engagement.
Community Management: Engaging with followers, managing comments, and building relationships with the audience.
Social Media Analytics: Tracking performance metrics such as reach, impressions, and engagement to refine strategies.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC advertising involves placing ads on search engines and other platforms where advertisers pay each time their ad is clicked. Skills needed include:
Campaign Creation: Setting up PPC campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads, including ad copywriting and keyword targeting.
Bid Management: Adjusting bids for keywords to optimize ad spend and ROI.
A/B Testing: Running experiments with different ad variations to determine which performs best.
PPC Analytics: Analyzing metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and cost-per-click (CPC) to evaluate and improve campaign performance.
Email Marketing
Email Campaign Design: Crafting engaging and persuasive email content and designing visually appealing templates.
List Management: Building and segmenting email lists to target specific audience groups effectively.
Automation: Setting up automated email workflows, such as welcome series, cart abandonment reminders, and drip campaigns.
Email Analytics: Tracking metrics such as open rates, click rates, and conversion rates to optimize email performance.
Data Analysis and Analytics
Data analysis is crucial for making informed decisions based on performance metrics. Important skills include:
Google Analytics: Proficiency in using Google Analytics to track website performance and user behavior.
Data Interpretation: Analyzing data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that inform marketing strategies.
Reporting: Creating detailed reports that communicate findings and recommendations to stakeholders.
Data Visualization: Using tools like Google Data Studio or Tableau to present data in a clear and actionable format.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
A/B Testing: Conducting tests to compare different versions of web pages or elements to see which performs better.
User Experience (UX) Design: Understanding how design choices impact user behavior and optimizing the user journey.
Landing Page Optimization: Designing and refining landing pages to maximize conversions.
Heatmaps and User Recording: Using tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg to visualize user interactions and identify areas for improvement.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation involves using software to automate repetitive tasks and workflows. Key skills are:
Tool Proficiency: Familiarity with platforms like HubSpot, Marketo, or Mailchimp for automating marketing processes.
Workflow Creation: Setting up and managing automated workflows for lead nurturing, customer engagement, and follow-ups.
Segmentation: Using automation to segment audiences based on behavior, demographics, or interactions.
Performance Tracking: Monitoring the effectiveness of automated campaigns and making adjustments as needed.
Web Development Basics
While not all digital marketers need to be expert developers, having a basic understanding of web development can be beneficial:
HTML/CSS: Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS for making minor updates or understanding how web pages are structured.
Content Management Systems (CMS): Familiarity with CMS platforms like WordPress or Shopify for managing and updating content.
Troubleshooting: Ability to identify and troubleshoot basic issues related to website performance or functionality.
Project Management
Project management skills help in planning, executing, and overseeing digital marketing campaigns. Essential skills include:
Organization: Keeping track of deadlines, deliverables, and resources for multiple projects.
Communication: Coordinating with team members, stakeholders, and clients effectively.
Budget Management: Managing marketing budgets and ensuring campaigns stay within financial constraints.
Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and managing time efficiently to meet project goals and deadlines.
Creativity and Innovation
Creativity is essential for developing unique marketing strategies and content that stand out in a crowded digital space. Skills include:
Creative Thinking: Generating new ideas and approaches for campaigns, content, and strategies.
Design Principles: Understanding basic design principles to create visually appealing content and ads.
Trend Awareness: Staying updated on industry trends and incorporating them into marketing strategies.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems help manage interactions with customers and prospects. Key skills include:
CRM Software Proficiency: Familiarity with CRM tools like Salesforce or Zoho to track and manage customer interactions.
Lead Management: Using CRM systems to manage and nurture leads through the sales funnel.
Customer Data Analysis: Analyzing customer data to personalize marketing efforts and improve customer experiences.
Ethics and Compliance
Ethics and compliance are crucial in ensuring that marketing practices are transparent and adhere to regulations. Skills include:
Data Privacy: Understanding and complying with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Ethical Marketing: Ensuring that marketing practices are honest, respectful, and do not mislead consumers.
Disclosure: Properly disclosing any sponsored content or partnerships in accordance with legal and ethical standards.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
The digital marketing landscape is ever-evolving, requiring professionals to be adaptable and committed to continuous learning. Skills include:
Staying Updated: Keeping abreast of new tools, technologies, and best practices in digital marketing.
Learning Agility: Quickly acquiring new skills and knowledge to respond to changes in the industry.
Problem-Solving: Adapting strategies and tactics in response to challenges or shifts in the market.
Conclusion
Digital marketing is a multifaceted field that requires a diverse skill set to be effective. From technical expertise in SEO and PPC to creative prowess in content creation and social media management, each skill contributes to a comprehensive digital marketing strategy. By developing and honing these skills, you can enhance your ability to create successful marketing campaigns and drive meaningful results for businesses or clients. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying updated and adaptable will be key to sustaining success in this dynamic field.